PADMAPADA
Wound and diabetic foot ecosystem
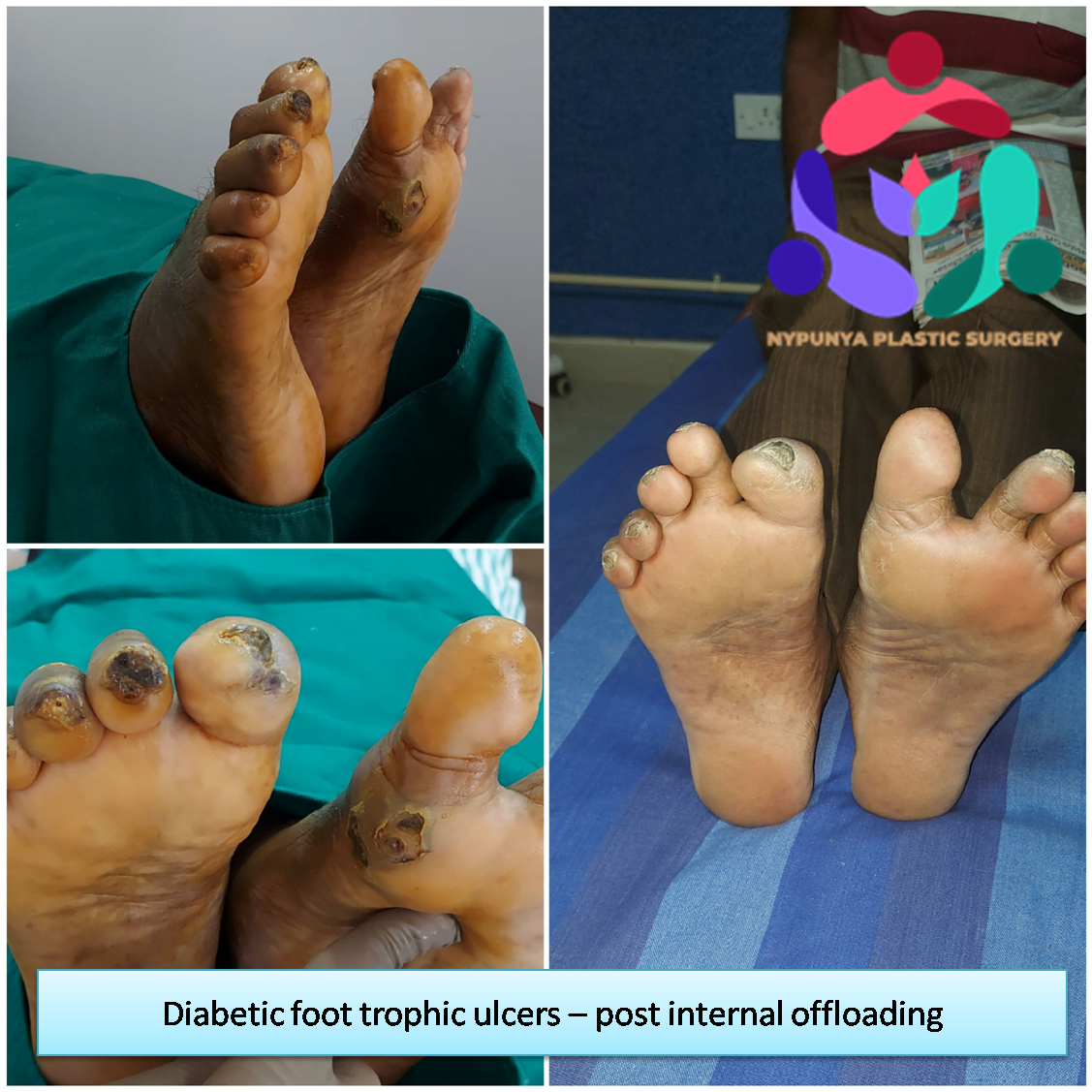
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound on the foot of a person with diabetes, most commonly located on the plantar surface, or bottom of the foot. Diabetic foot ulcers occur in approximately 15% of persons with diabetes. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, 6% will be hospitalised due to infection or other ulcer-related complications. The risk of foot ulceration and limb amputation increases with age and the duration of diabetes. Diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations. Between 14-24% percent of patients with diabetes who develop a foot ulcer will require an amputation. The good news is that a foot ulcer is preventable if the underlying conditions causing it, diabetic peripheral neuropathy and/or peripheral arterial disease, are appropriately diagnosed and treated.
Causes of diabetic foot
Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) causing loss of protective sensations and foot deformity along with this lower extremity ischemia (lack of blood flow) due to peripheral artery disease are the primary causes of diabetic foot ulcers.
End to end solution for chronic wound and diabetic foot care
A chain of super specialty chronic wound and diabetic foot care clinics providing multidisciplinary care under one roof.
We manage - Chronic wounds, venous ulcers, arterial ulcers traumatic wounds, Diabetic Foot Conditions, lymphedema foot conditions
We have end-to-end solutions from “wound and foot diagnostics - Surgical Treatment- Advanced wound care systems and products - Customised Orthotics - Therapeutic Footwear
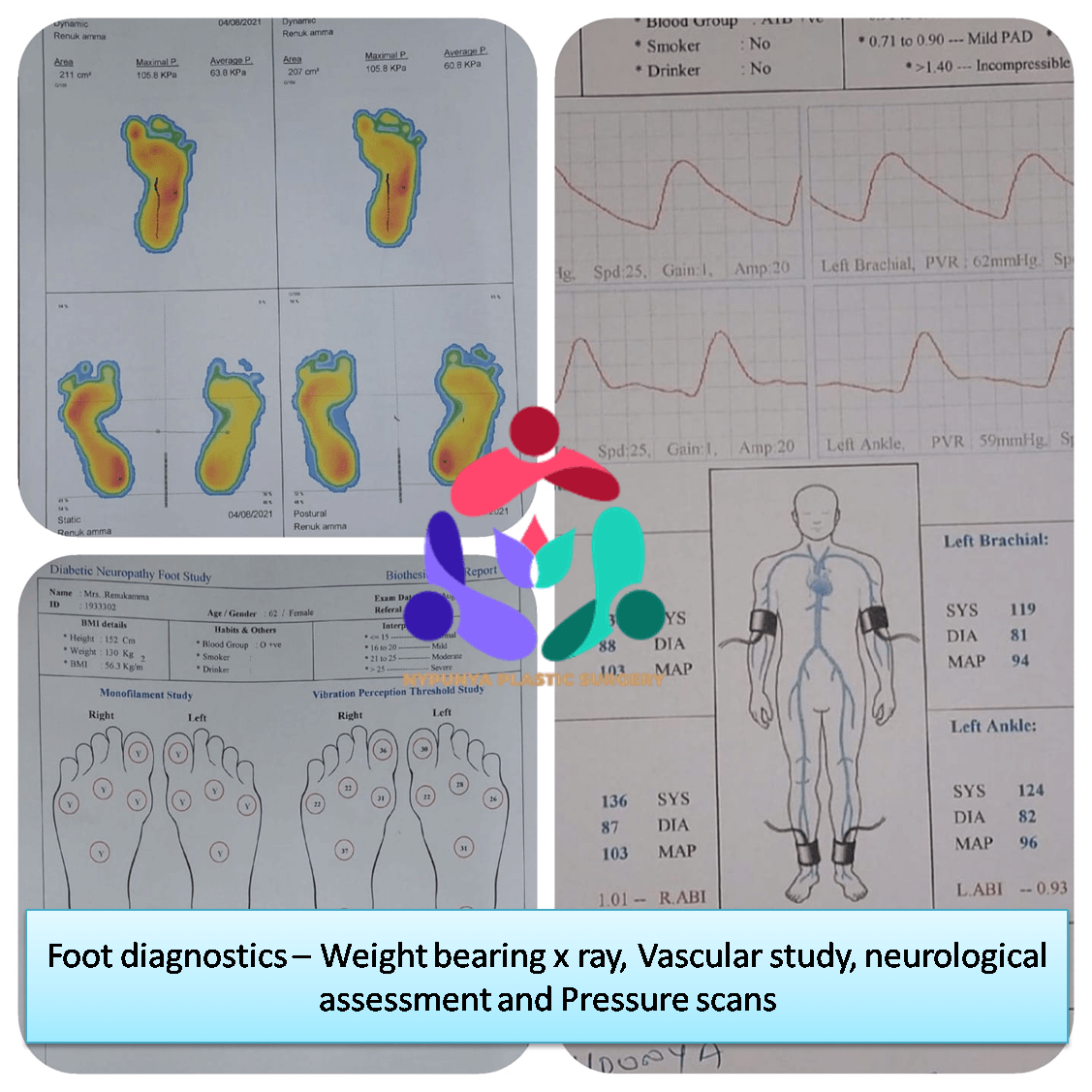
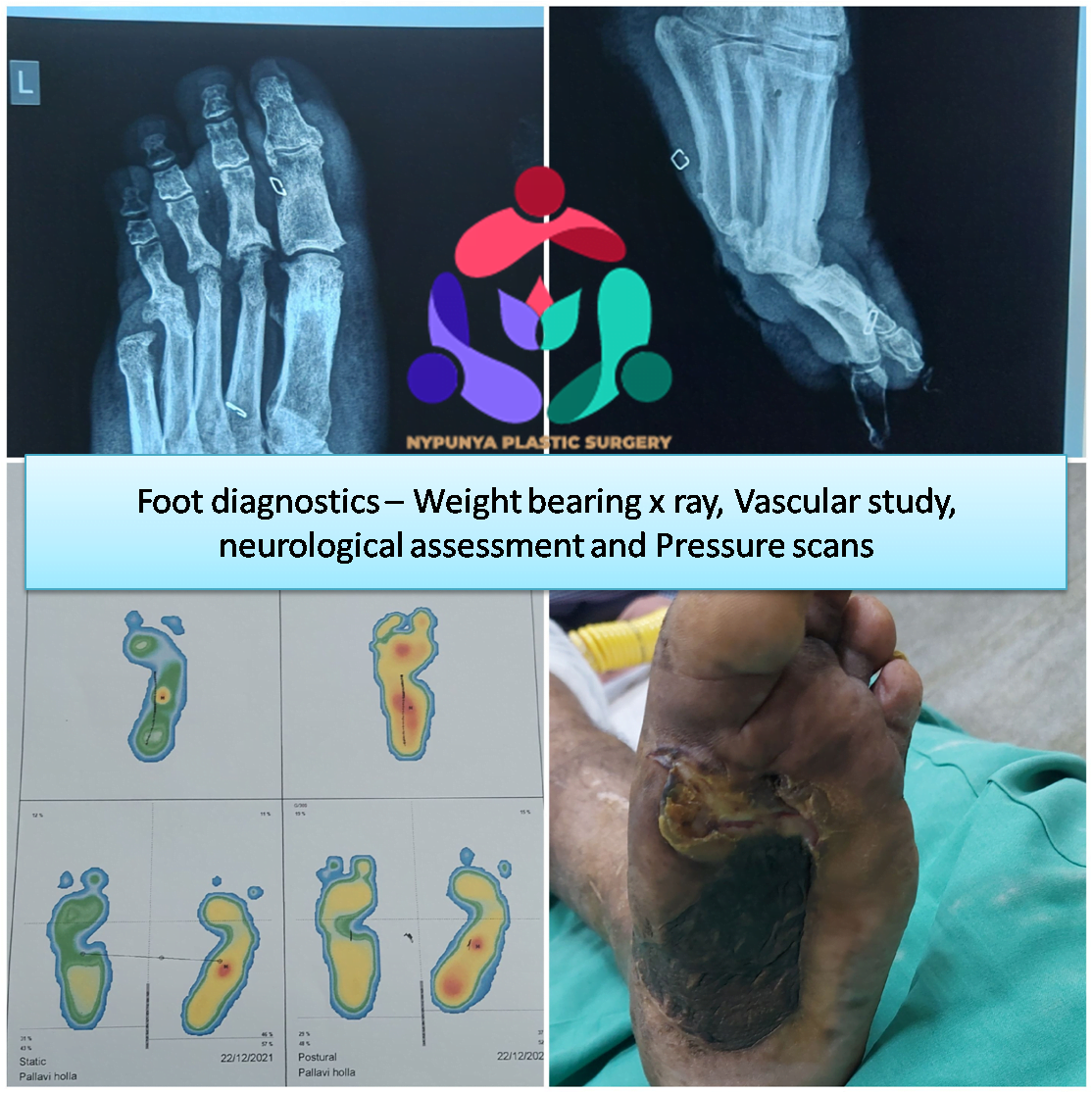
- 3D Foot Scan
- Weight bearing x rays
- Neuropathy Assessment
- Oxygen Perfusion Assessment
- Plantar Pressure Scan
- Vascular Assessment
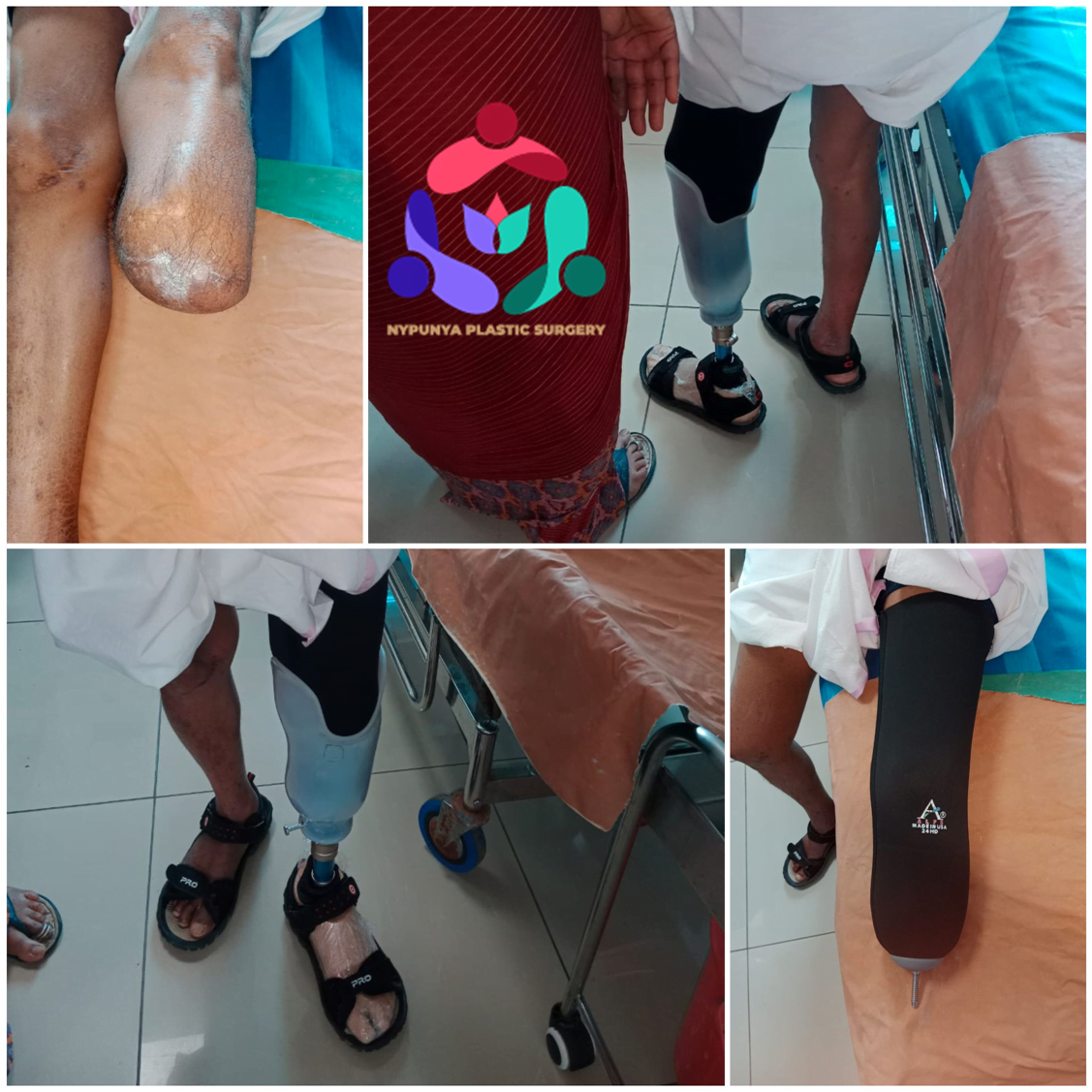
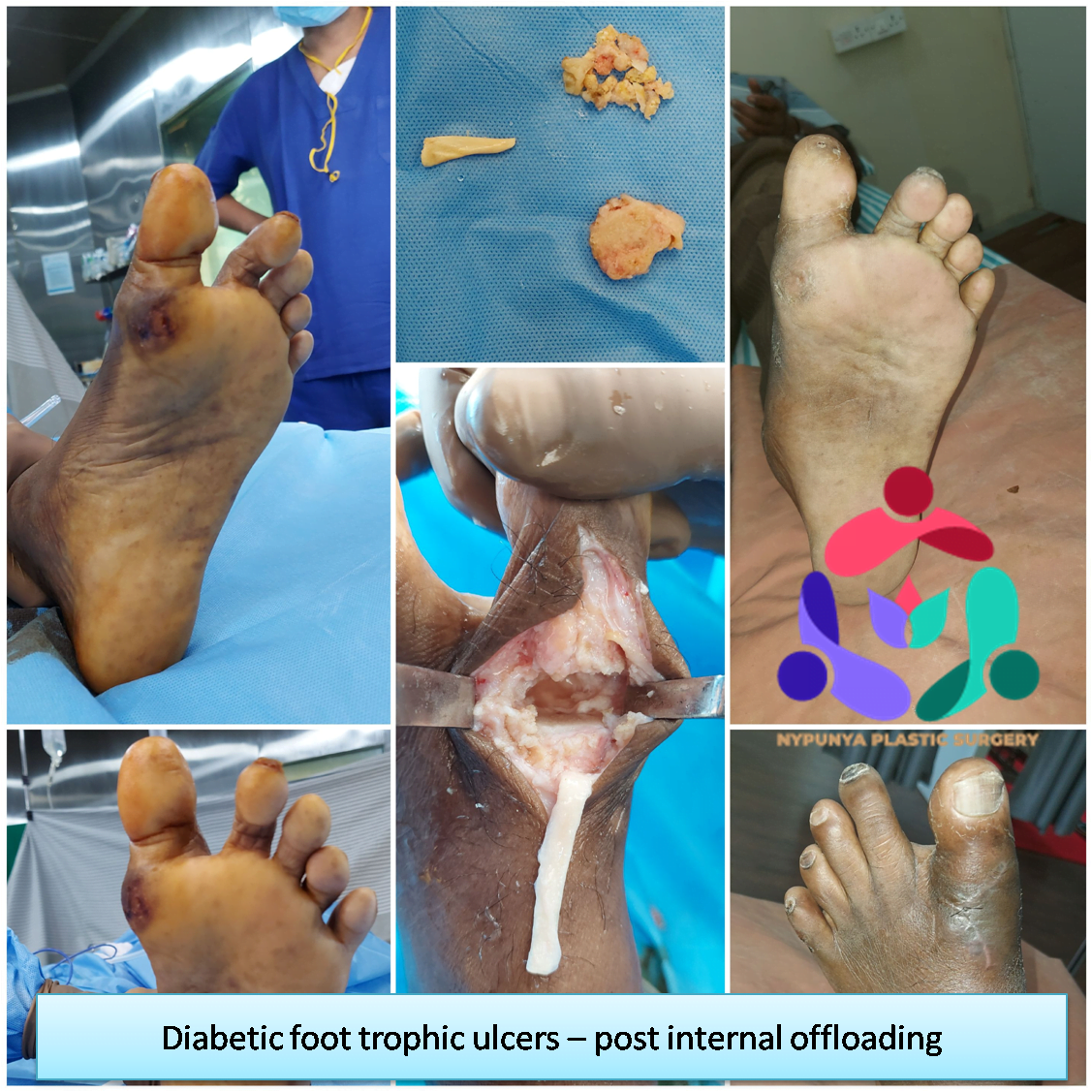
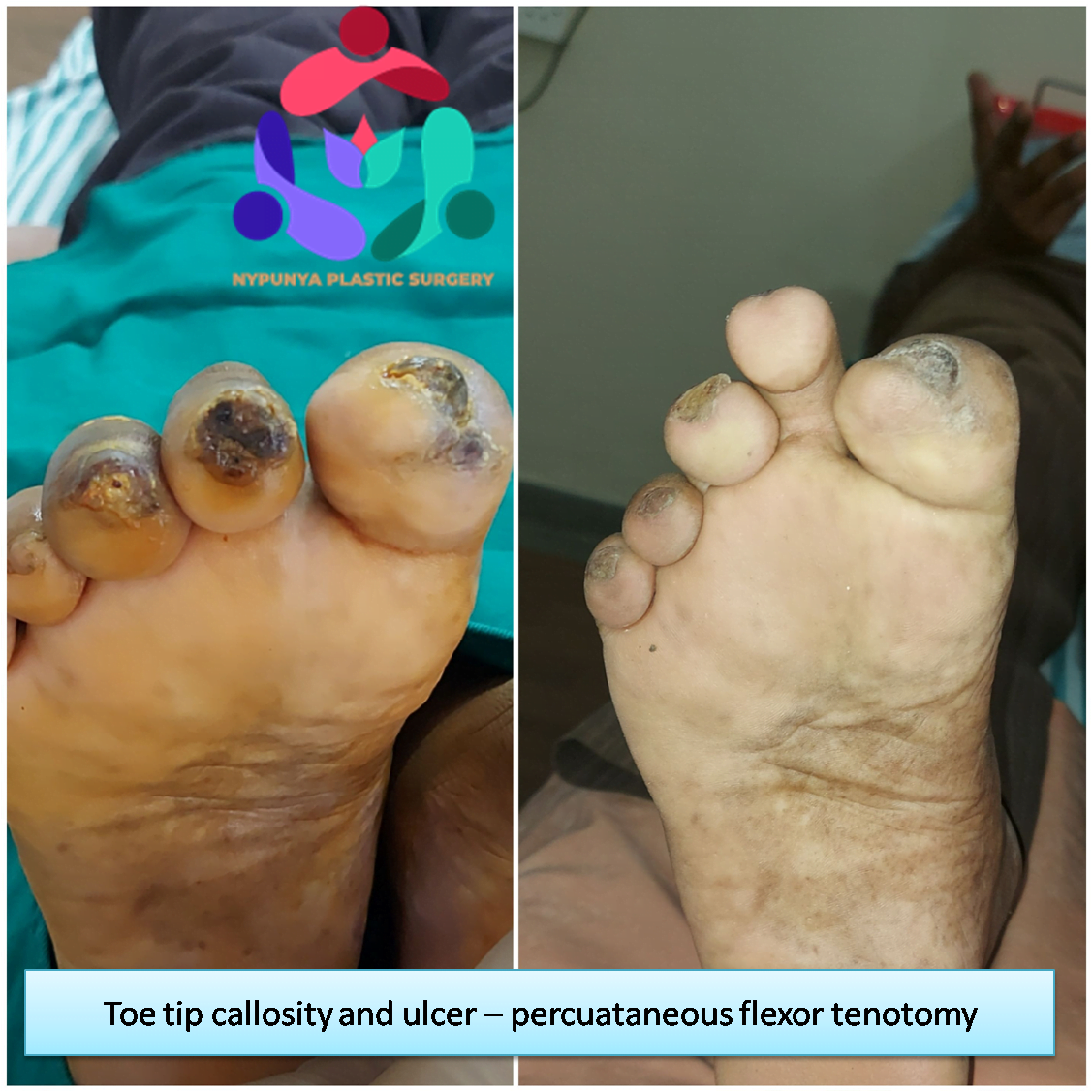
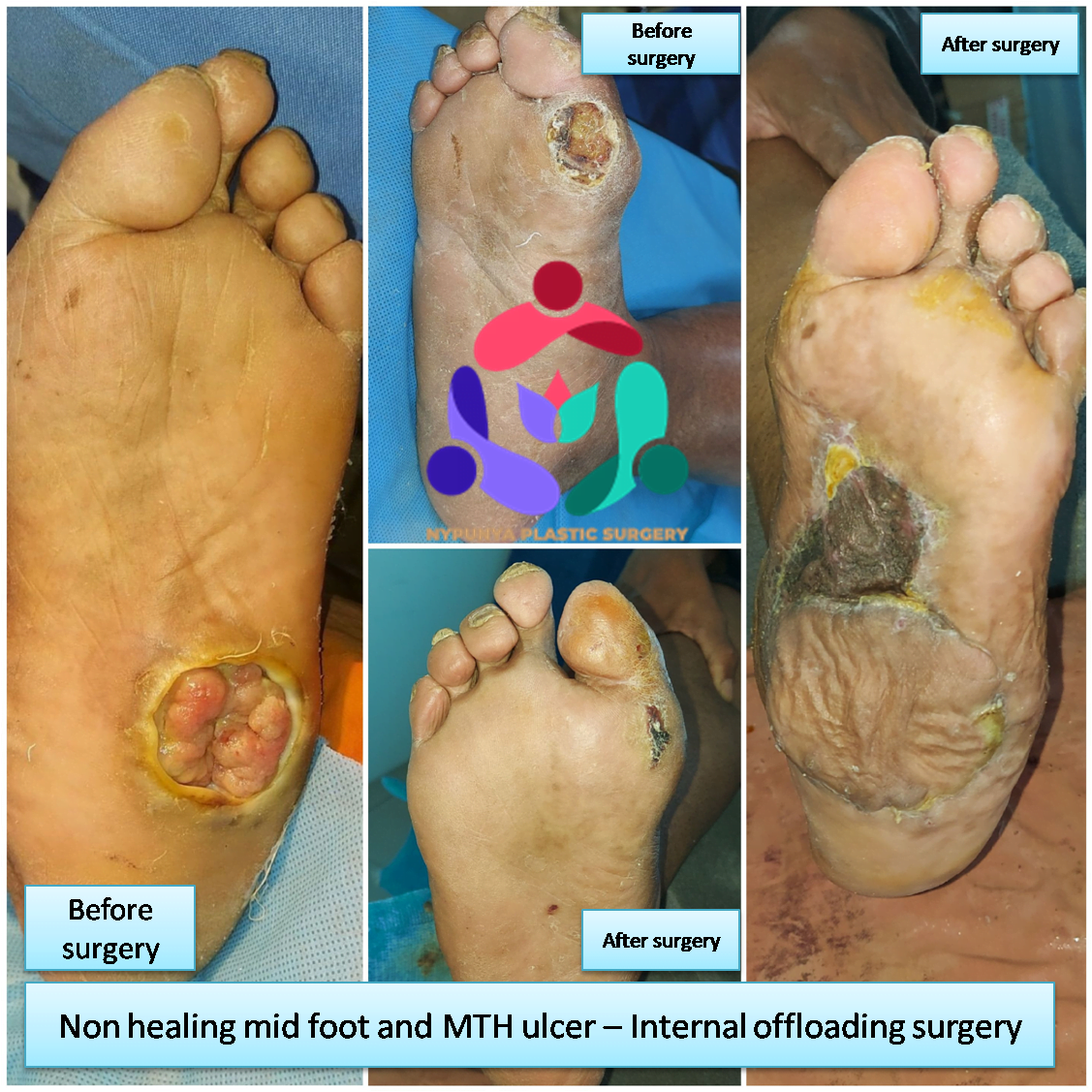
- Offloading Surgeries
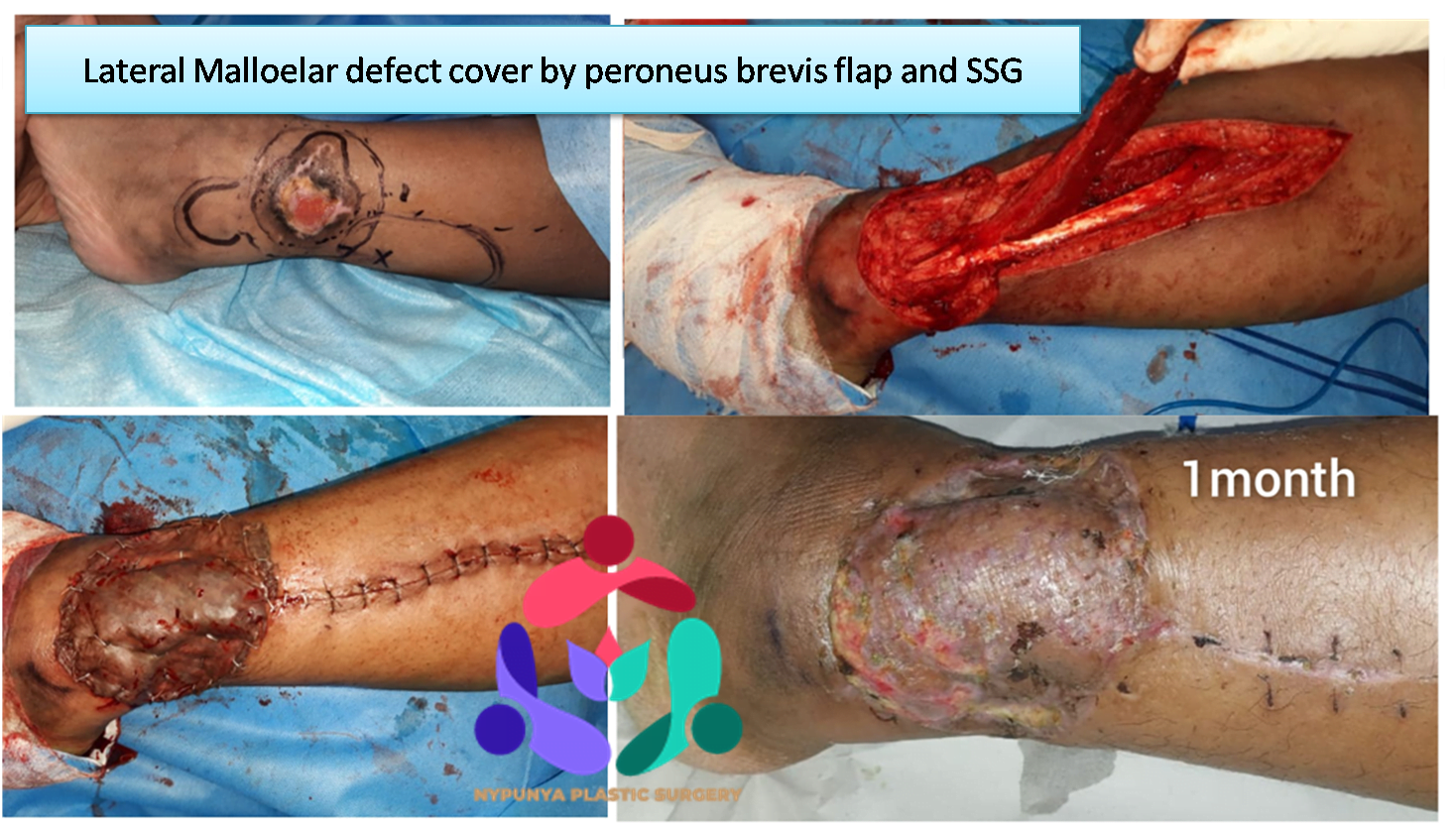
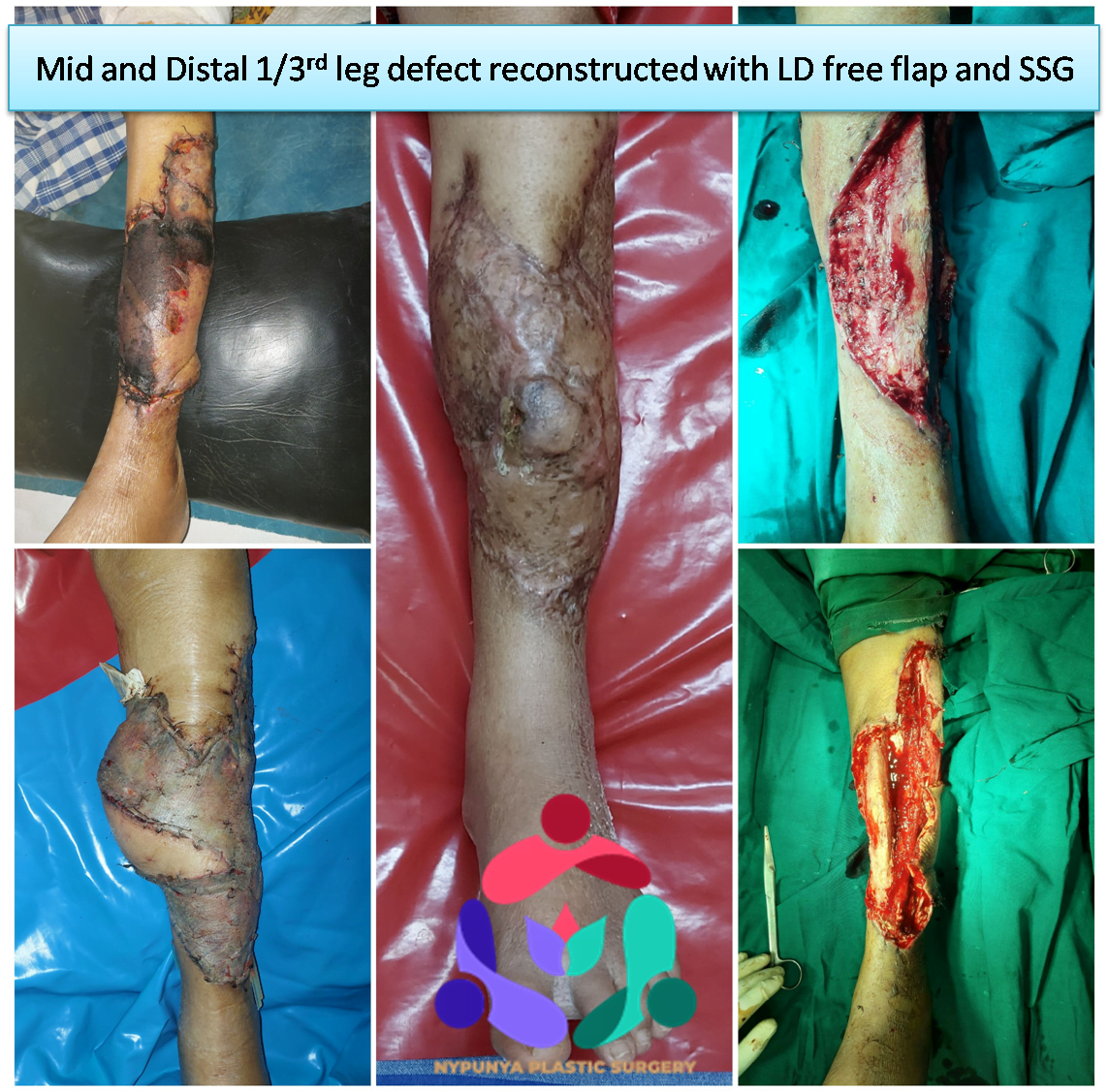
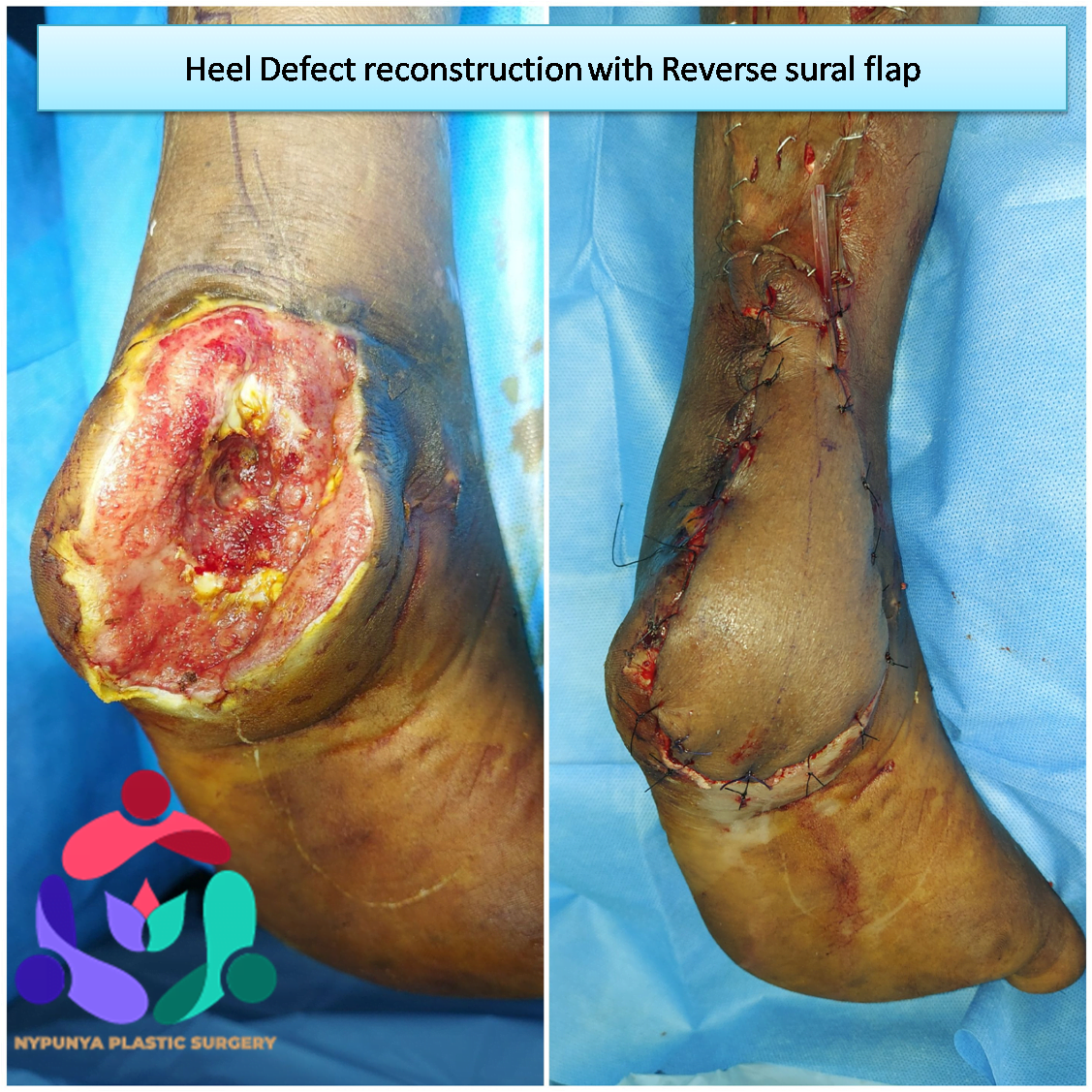
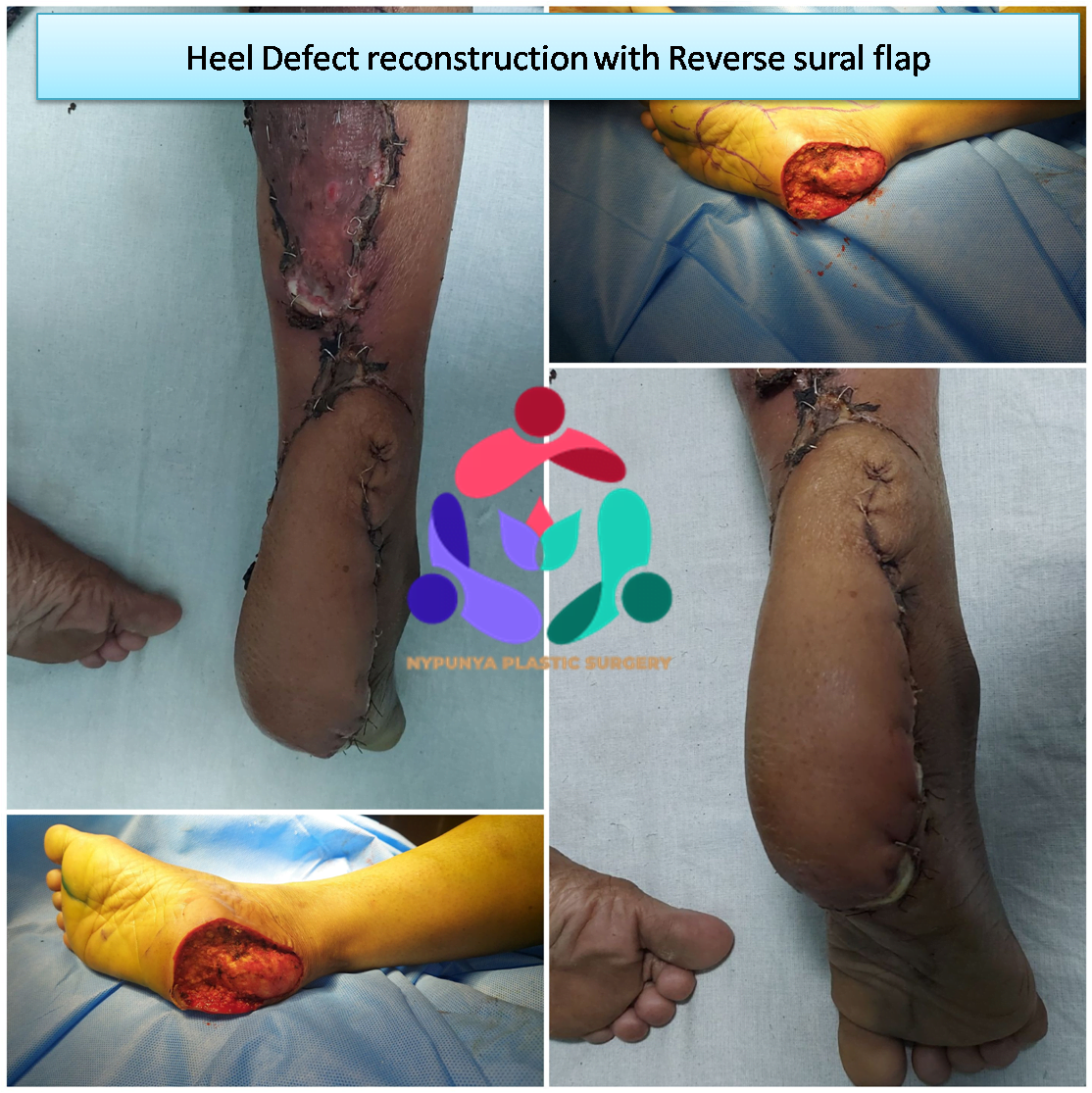
- Surgeries related to Wound Grafts and vascularised flaps
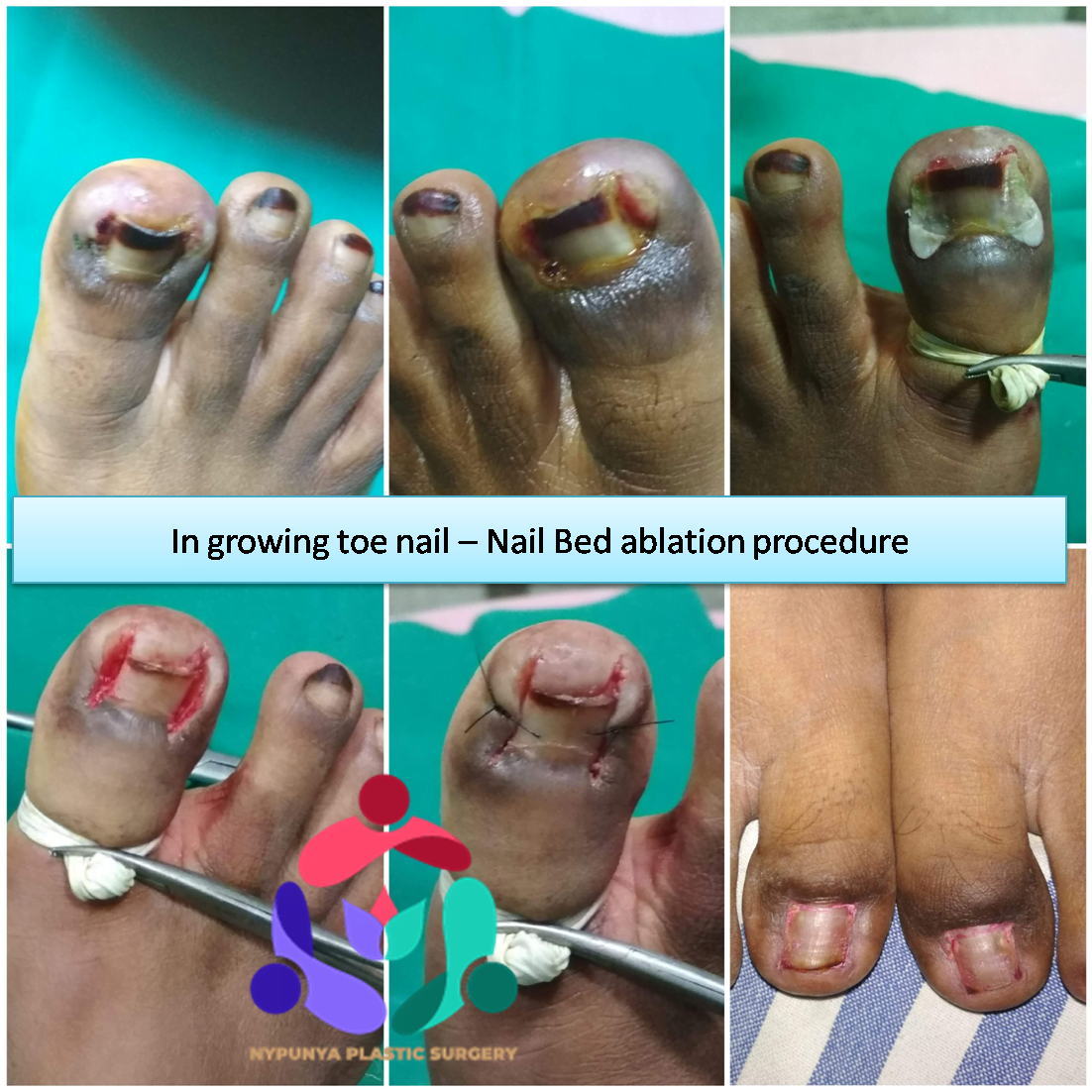
- Callus & Corn Excisions
- Varicose Veins surgery
- Lower Limb Angioplasty
- Deformity Corrections
- Amputations
- Oxygen therapy
- Negative pressure VAC therapy
- Amniotic products in wound care
- PRP and PRFM in wound care
- Acellular dermal matrices
- Plasma charged wound wash
Types of Diabetic Ulcers
- Neuropathic ulcers occur where there is peripheral diabetic neuropathy, but no ischemia caused by peripheral artery disease.
- Ischemic ulcers occur where there is peripheral artery disease present without the involvement of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
- Neuroischemic ulcers occur where the person has both peripheral neuropathy and ischemia resulting from peripheral artery disease.
- Infected diabetic Ulcers occur when any of the above conditions is left unattended.
Types of Treatment
Treatment usually consists of:
- Optimal glucose control.
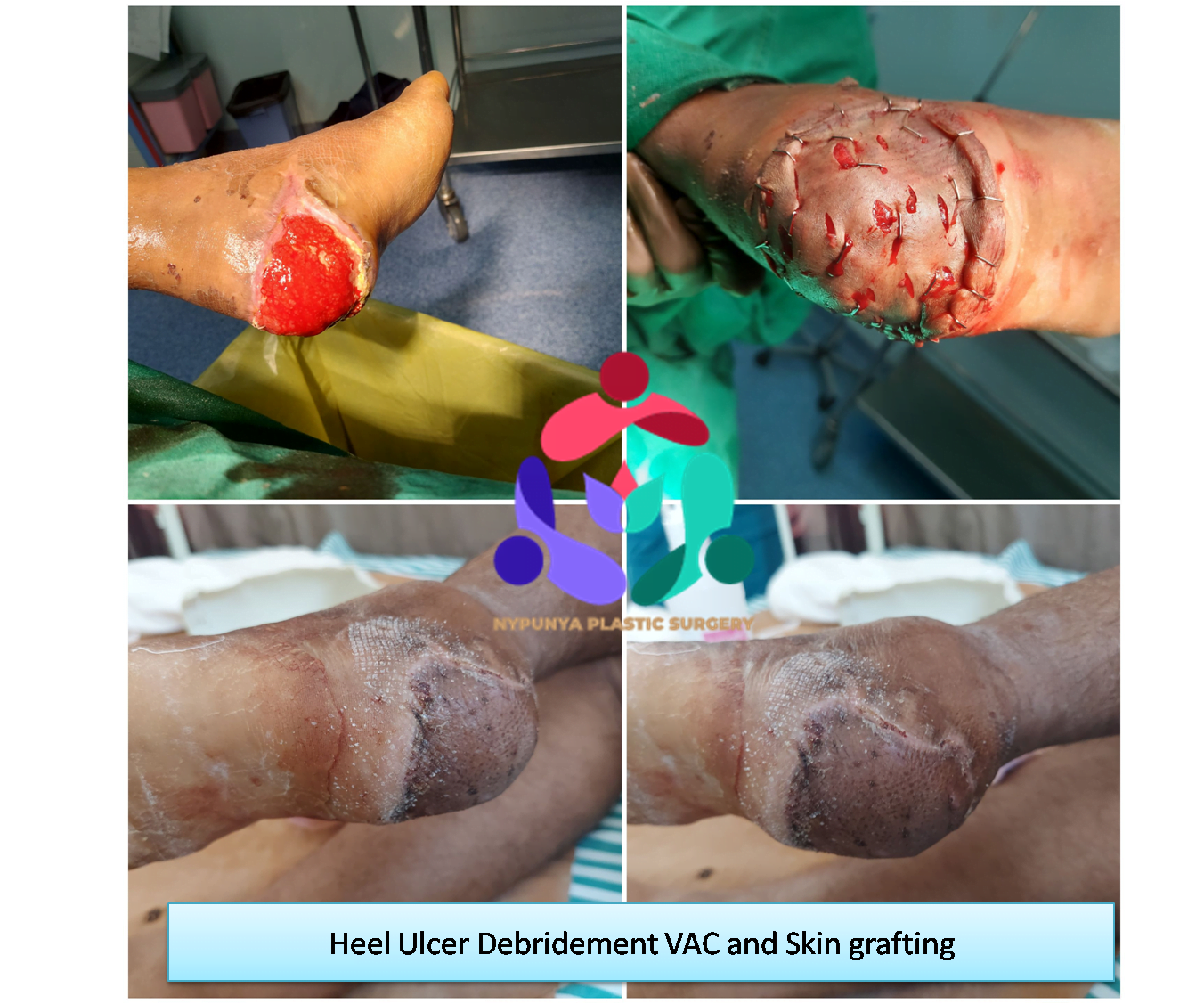
- Debridement - removal of all hyperkeratotic (thickened) skin, infected and nonviable, including necrotic (dead), tissue, slough, foreign debris, and residual material from dressings.
- Systemic antibiotics for deep infection, drainage, and cellulitis.
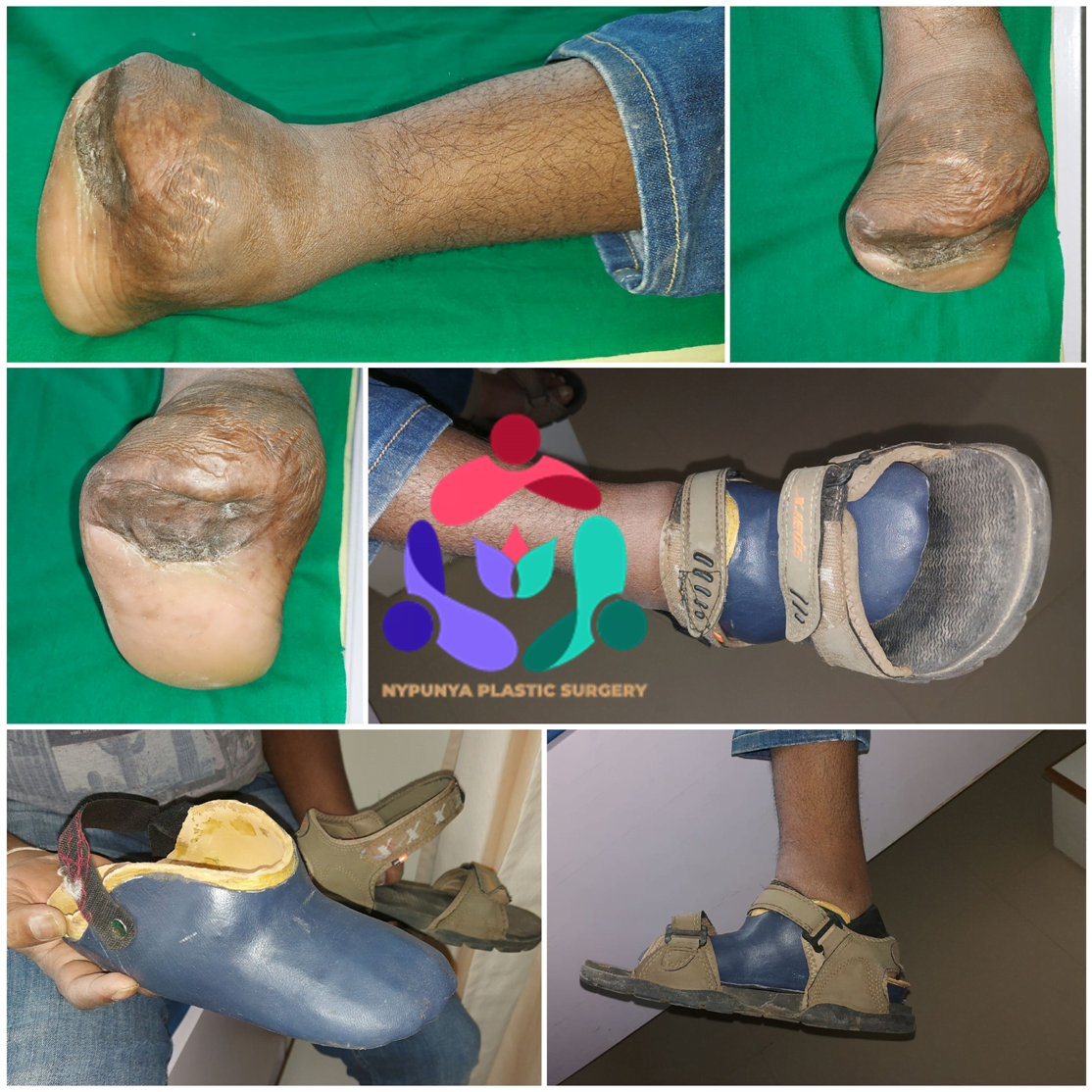
- Off-loading - Relieving the pressure from the ulcerated areas by having the patient wear special foot gear, a brace, specialized castings, or using a wheelchair or crutches.
- Creating a moist wound environment and VAC dressings
- Treatment with growth factors and/or cellular therapy if the wound is not healing.
Wound Care
- Wounds and ulcers heal faster and have a lower risk of infection if they are kept covered and moist, using dressings and topically-applied medications.
- Products including saline, growth factors, ulcer dressings, and skin substitutes are highly effective in healing foot ulcers.
- There should be adequate circulation to the ulcerated area.
- Tight control of blood glucose is critical during to the effect treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer. This will enhance healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Surgical Options
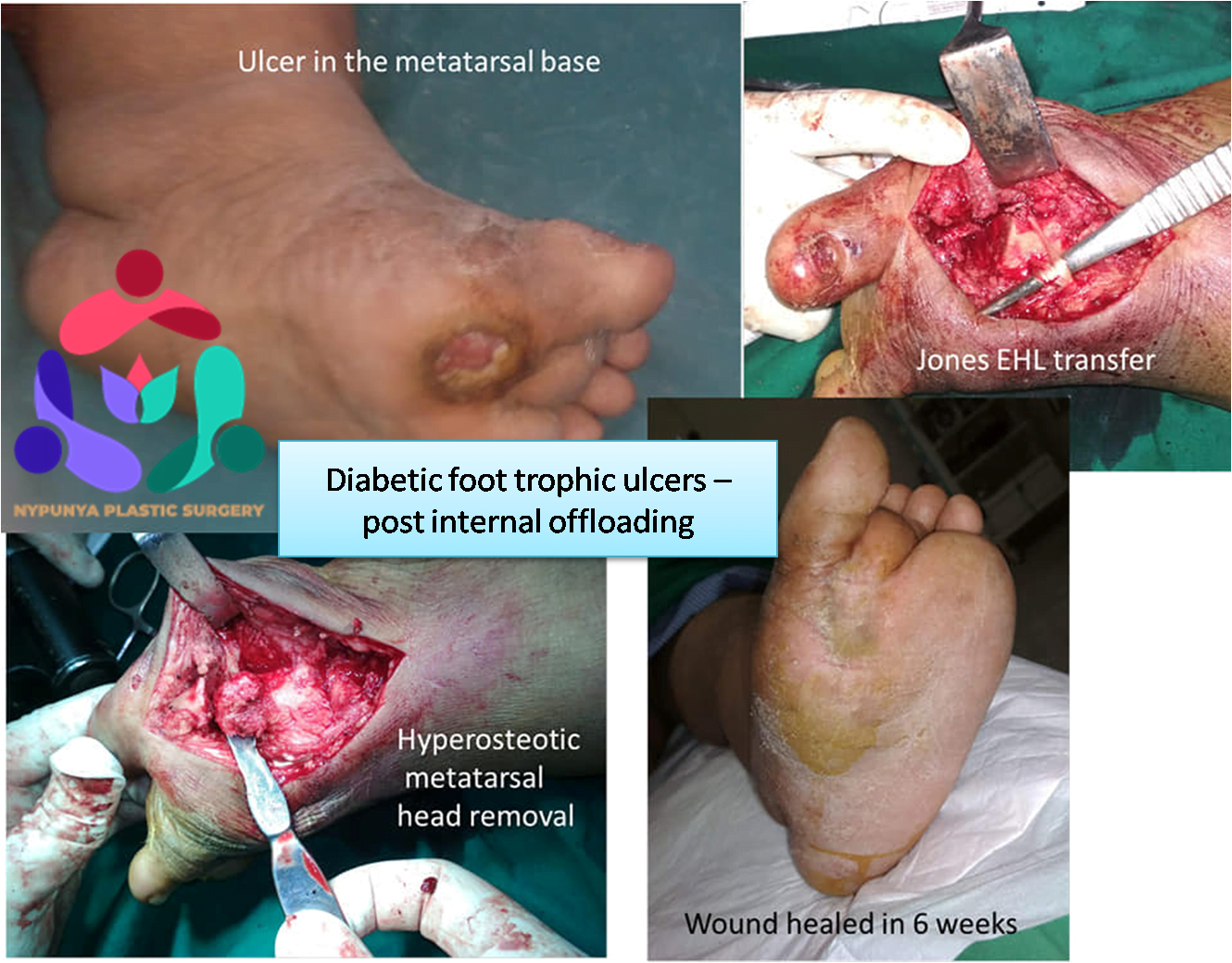
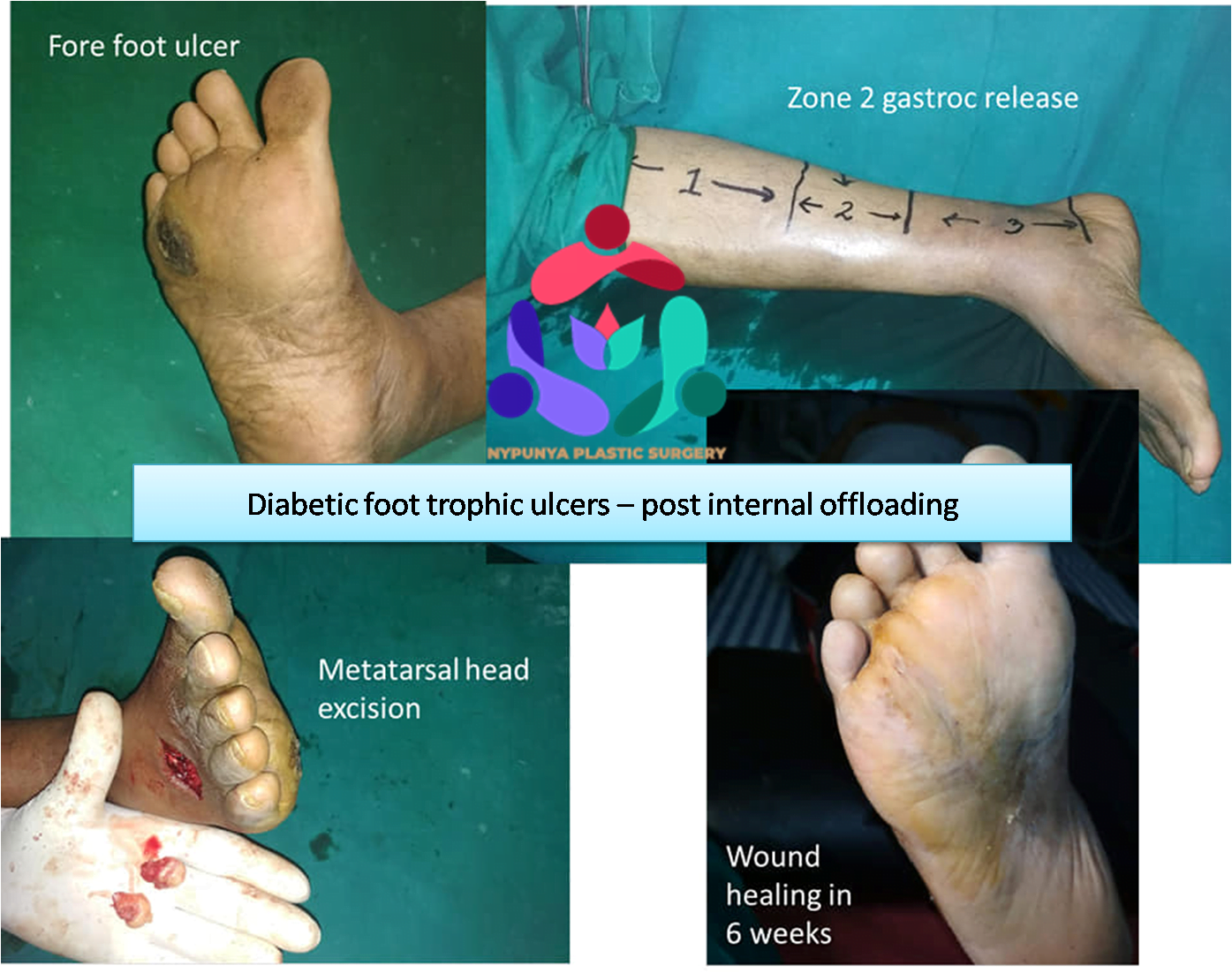
- Remove pressure on the affected area, including shaving or excision of bone(s) and preventive offloading surgeries.
- Correct deformities, such as hammertoes, bunions, or bony “bumps.”
- Treat infections such as osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone, by surgically removing the infected bone.
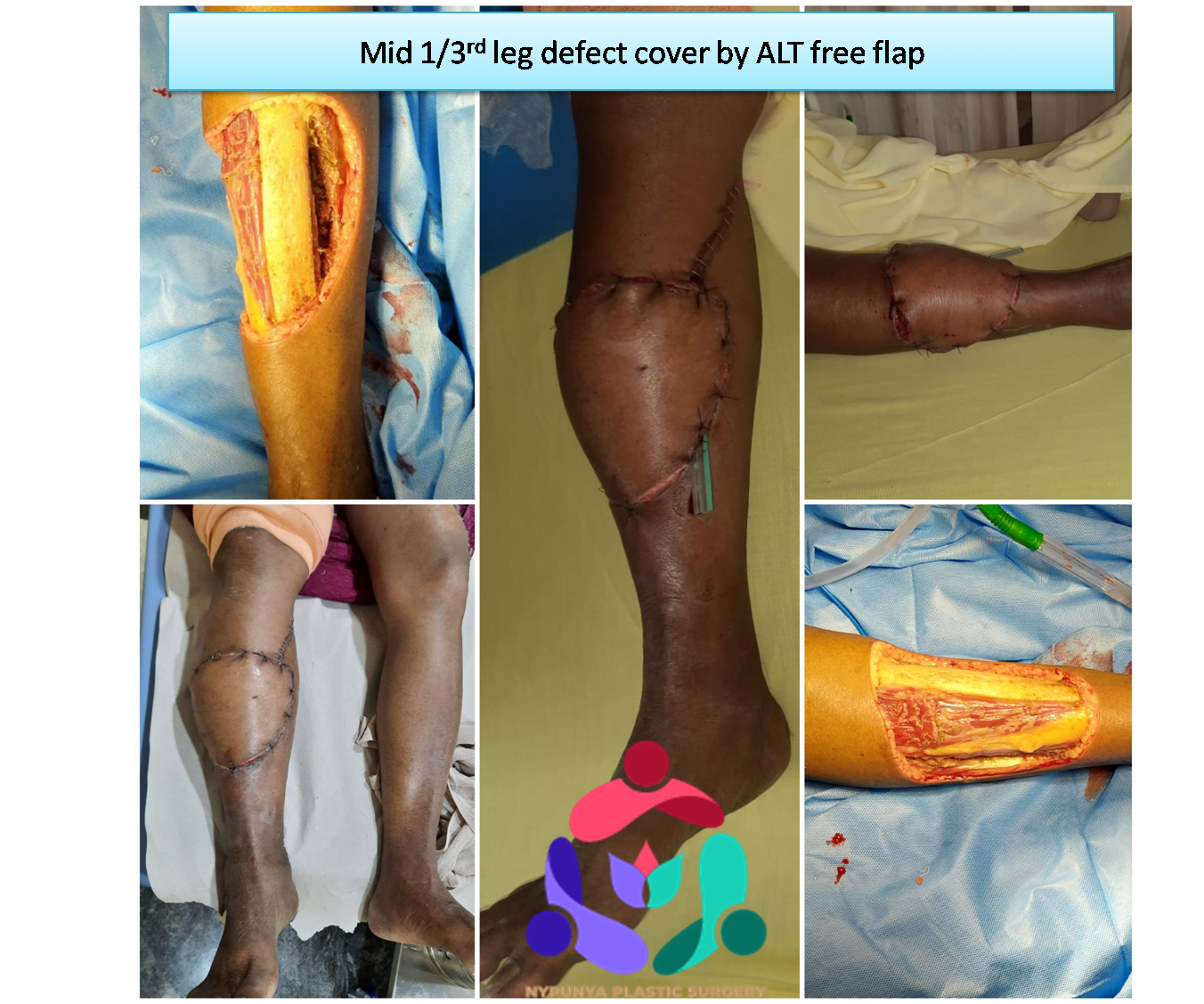
- Use Skin grafts and vascularized tissue transfer to cover wounds.
The risk of developing a foot ulcer can be reduced by:
- Smoking cessation
- Lowering consumption of alcohol
- Reducing high cholesterol
- Controlling blood glucose levels
- Wearing the appropriate shoes and socks
- Inspecting feet every day—especially the sole and between the toes—for cuts, bruises, cracks, blisters, redness, ulcers, and other signs of abnormality
Get an appointment
please fill form below to get in touch with us